반응형
15-2 소득 예측 모델 만들기
의사결정나무 모델 만들기
모델 설정하기
모델 만들기
from sklearn import tree
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 1234, # 난수 고정
max_depth = 3) # 나무 깊이
train_x = df_train.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
train_y = df_train['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
model = clf.fit(X = train_x, y = train_y) # 모델 만들기모델 구조 살펴보기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.dpi' : '100', # 그래프 크기 설정
'figure.figsize' : [12, 8]}) # 해상도 설정
tree.plot_tree(model); # 그래프 출력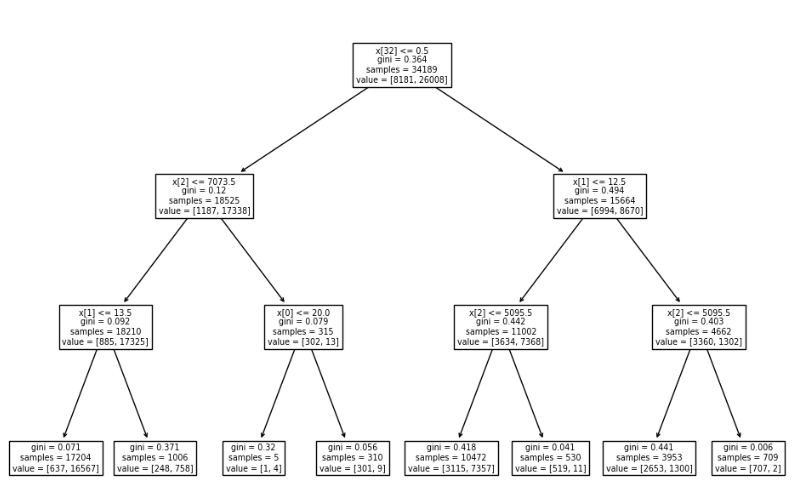
tree.plot_tree(model,
feature_names = train_x.columns, # 예측 변수명
class_names = ['high', 'low'], # 타겟 변수 클래스, 알파벳순
proportion = True, # 비율 표기
filled = True, # 색칠
rounded = True, # 둥근 테두리
impurity = False, # 불순도 표시
label = 'root', # label 표시 위치
fontsize = 10); # 글자 크기
모델을 이용해 예측하기
test_x = df_test.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
test_y = df_test['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
# 예측값 구하기
df_test['pred'] = model.predict(test_x)
df_test
성능 평가하기
confusion matrix 만들기
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
labels = ['high', 'low']) # 클래스 배치 순서
conf_mat
"""
array([[ 1801, 1705],
[ 582, 10565]])
"""plt.rcParams.update(plt.rcParamsDefault) # 그래프 설정 되돌리기from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
p = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix = conf_mat, # 컨퓨전 매트릭스
display_labels = ('high', 'low')) # 타겟 변수 클래스명
p.plot(cmap = 'Blues') # 컬러맵 적용해 출력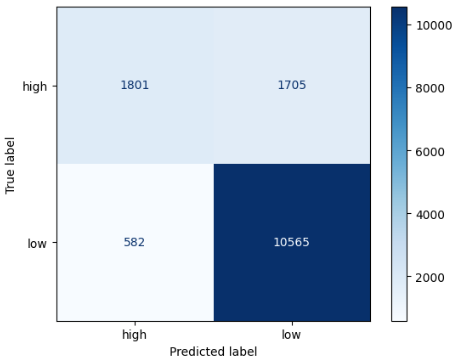
성능 평가 지표 구하기
- 정확도(accuracy): 모델이 예측해서 맞춘 비율
- 정밀도(precision): 모델이 관심 클래스를 예측해서 맞춘 비율
- 재현율(recall): 모델이 실제 데이터에서 관심 클래스를 찾아낸 비율
- F1 score: recall과 precision의 크기를 함께 반영한 것
# accuracy
import sklearn.metrics as metrics
metrics.accuracy_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred']) # 예측값
##출력: 0.8439227461953184# precision
metrics.precision_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
##출력: 0.7557700377675199# recall
metrics.recall_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
##출력: 0.5136908157444381# F1 score
metrics.f1_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
##출력: 0.6116488368143997성능 평가 지표 사용
- accuracy: 모델의 일반적인 성능을 나타내므로 항상 살펴봐야 함
- precision: 관심 클래스가 분명할 때
- recall: 관심 클래스를 최대한 많이 찾아내야 할 때
- F1 score: recall과 precision이 모두 중요할 때
정리하기
15 머신러닝을 이용한 예측 분석
15-1 머신러닝 모델 알아보기
15-2 소득 예측 모델 만들기
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('adult.csv')
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Data columns (total 15 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 age 48842 non-null int64
1 workclass 48842 non-null object
2 fnlwgt 48842 non-null int64
3 education 48842 non-null object
4 education_num 48842 non-null int64
5 marital_status 48842 non-null object
6 occupation 48842 non-null object
7 relationship 48842 non-null object
8 race 48842 non-null object
9 sex 48842 non-null object
10 capital_gain 48842 non-null int64
11 capital_loss 48842 non-null int64
12 hours_per_week 48842 non-null int64
13 native_country 48842 non-null object
14 income 48842 non-null object
dtypes: int64(6), object(9)
memory usage: 5.6+ MB
전처리하기
1. 타겟 변수 전처리
df['income'].value_counts(normalize = True)
<=50K 0.760718
>50K 0.239282
Name: income, dtype: float64
import numpy as np
df['income'] = np.where(df['income'] == '>50K', 'high', 'low')
df['income'].value_counts(normalize = True)
low 0.760718
high 0.239282
Name: income, dtype: float64
2. 불필요한 변수 제거하기
df = df.drop(columns = 'fnlwgt')
3. 문자 타입 변수를 숫자 타입으로 바꾸기
원핫 인코딩하기
df_tmp = df[['sex']]
df_tmp.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Data columns (total 1 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 sex 48842 non-null object
dtypes: object(1)
memory usage: 381.7+ KB
df_tmp['sex'].value_counts()
Male 32650
Female 16192
Name: sex, dtype: int64
# df_tmp의 문자 타입 변수에 원핫 인코딩 적용
df_tmp = pd.get_dummies(df_tmp)
df_tmp.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 sex_Female 48842 non-null uint8
1 sex_Male 48842 non-null uint8
dtypes: uint8(2)
memory usage: 95.5 KB
df_tmp[['sex_Female', 'sex_Male']].head()
sex_Female sex_Male
0 0 1
1 0 1
2 0 1
3 0 1
4 1 0
target = df['income'] # income 추출
df = df.drop(columns = 'income') # income 제거
df = pd.get_dummies(df) # 문자 타입 변수 원핫 인코딩
df['income'] = target # df에 target 삽입
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Columns: 108 entries, age to income
dtypes: int64(5), object(1), uint8(102)
memory usage: 7.0+ MB
import numpy as np
df.info(max_cols = np.inf)
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Data columns (total 108 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 age 48842 non-null int64
1 education_num 48842 non-null int64
2 capital_gain 48842 non-null int64
3 capital_loss 48842 non-null int64
4 hours_per_week 48842 non-null int64
5 workclass_? 48842 non-null uint8
6 workclass_Federal-gov 48842 non-null uint8
7 workclass_Local-gov 48842 non-null uint8
8 workclass_Never-worked 48842 non-null uint8
9 workclass_Private 48842 non-null uint8
10 workclass_Self-emp-inc 48842 non-null uint8
11 workclass_Self-emp-not-inc 48842 non-null uint8
12 workclass_State-gov 48842 non-null uint8
13 workclass_Without-pay 48842 non-null uint8
14 education_10th 48842 non-null uint8
15 education_11th 48842 non-null uint8
16 education_12th 48842 non-null uint8
17 education_1st-4th 48842 non-null uint8
18 education_5th-6th 48842 non-null uint8
19 education_7th-8th 48842 non-null uint8
20 education_9th 48842 non-null uint8
21 education_Assoc-acdm 48842 non-null uint8
22 education_Assoc-voc 48842 non-null uint8
23 education_Bachelors 48842 non-null uint8
24 education_Doctorate 48842 non-null uint8
25 education_HS-grad 48842 non-null uint8
26 education_Masters 48842 non-null uint8
27 education_Preschool 48842 non-null uint8
28 education_Prof-school 48842 non-null uint8
29 education_Some-college 48842 non-null uint8
30 marital_status_Divorced 48842 non-null uint8
31 marital_status_Married-AF-spouse 48842 non-null uint8
32 marital_status_Married-civ-spouse 48842 non-null uint8
33 marital_status_Married-spouse-absent 48842 non-null uint8
34 marital_status_Never-married 48842 non-null uint8
35 marital_status_Separated 48842 non-null uint8
36 marital_status_Widowed 48842 non-null uint8
37 occupation_? 48842 non-null uint8
38 occupation_Adm-clerical 48842 non-null uint8
39 occupation_Armed-Forces 48842 non-null uint8
40 occupation_Craft-repair 48842 non-null uint8
41 occupation_Exec-managerial 48842 non-null uint8
42 occupation_Farming-fishing 48842 non-null uint8
43 occupation_Handlers-cleaners 48842 non-null uint8
44 occupation_Machine-op-inspct 48842 non-null uint8
45 occupation_Other-service 48842 non-null uint8
46 occupation_Priv-house-serv 48842 non-null uint8
47 occupation_Prof-specialty 48842 non-null uint8
48 occupation_Protective-serv 48842 non-null uint8
49 occupation_Sales 48842 non-null uint8
50 occupation_Tech-support 48842 non-null uint8
51 occupation_Transport-moving 48842 non-null uint8
52 relationship_Husband 48842 non-null uint8
53 relationship_Not-in-family 48842 non-null uint8
54 relationship_Other-relative 48842 non-null uint8
55 relationship_Own-child 48842 non-null uint8
56 relationship_Unmarried 48842 non-null uint8
57 relationship_Wife 48842 non-null uint8
58 race_Amer-Indian-Eskimo 48842 non-null uint8
59 race_Asian-Pac-Islander 48842 non-null uint8
60 race_Black 48842 non-null uint8
61 race_Other 48842 non-null uint8
62 race_White 48842 non-null uint8
63 sex_Female 48842 non-null uint8
64 sex_Male 48842 non-null uint8
65 native_country_? 48842 non-null uint8
66 native_country_Cambodia 48842 non-null uint8
67 native_country_Canada 48842 non-null uint8
68 native_country_China 48842 non-null uint8
69 native_country_Columbia 48842 non-null uint8
70 native_country_Cuba 48842 non-null uint8
71 native_country_Dominican-Republic 48842 non-null uint8
72 native_country_Ecuador 48842 non-null uint8
73 native_country_El-Salvador 48842 non-null uint8
74 native_country_England 48842 non-null uint8
75 native_country_France 48842 non-null uint8
76 native_country_Germany 48842 non-null uint8
77 native_country_Greece 48842 non-null uint8
78 native_country_Guatemala 48842 non-null uint8
79 native_country_Haiti 48842 non-null uint8
80 native_country_Holand-Netherlands 48842 non-null uint8
81 native_country_Honduras 48842 non-null uint8
82 native_country_Hong 48842 non-null uint8
83 native_country_Hungary 48842 non-null uint8
84 native_country_India 48842 non-null uint8
85 native_country_Iran 48842 non-null uint8
86 native_country_Ireland 48842 non-null uint8
87 native_country_Italy 48842 non-null uint8
88 native_country_Jamaica 48842 non-null uint8
89 native_country_Japan 48842 non-null uint8
90 native_country_Laos 48842 non-null uint8
91 native_country_Mexico 48842 non-null uint8
92 native_country_Nicaragua 48842 non-null uint8
93 native_country_Outlying-US(Guam-USVI-etc) 48842 non-null uint8
94 native_country_Peru 48842 non-null uint8
95 native_country_Philippines 48842 non-null uint8
96 native_country_Poland 48842 non-null uint8
97 native_country_Portugal 48842 non-null uint8
98 native_country_Puerto-Rico 48842 non-null uint8
99 native_country_Scotland 48842 non-null uint8
100 native_country_South 48842 non-null uint8
101 native_country_Taiwan 48842 non-null uint8
102 native_country_Thailand 48842 non-null uint8
103 native_country_Trinadad&Tobago 48842 non-null uint8
104 native_country_United-States 48842 non-null uint8
105 native_country_Vietnam 48842 non-null uint8
106 native_country_Yugoslavia 48842 non-null uint8
107 income 48842 non-null object
dtypes: int64(5), object(1), uint8(102)
memory usage: 7.0+ MB
import numpy as np
df.iloc[:,0:6].info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 48842 entries, 0 to 48841
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 age 48842 non-null int64
1 education_num 48842 non-null int64
2 capital_gain 48842 non-null int64
3 capital_loss 48842 non-null int64
4 hours_per_week 48842 non-null int64
5 workclass_? 48842 non-null uint8
dtypes: int64(5), uint8(1)
memory usage: 1.9 MB
4. 데이터 분할하기
adult 데이터 분할하기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
df_train, df_test = train_test_split(df,
test_size = 0.3, # 테스트 세트 비율
stratify = df['income'], # 타겟 변수 비율 유지
random_state = 1234) # 난수 고정
# train
df_train.shape
(34189, 108)
# test
df_test.shape
(14653, 108)
# train
df_train['income'].value_counts(normalize = True)
low 0.760713
high 0.239287
Name: income, dtype: float64
# test
df_test['income'].value_counts(normalize = True)
low 0.760732
high 0.239268
Name: income, dtype: float64
의사결정나무 모델 만들기
모델 설정하기
from sklearn import tree
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 1234, # 난수 고정
max_depth = 3) # 나무 깊이
모델 만들기
train_x = df_train.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
train_y = df_train['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
model = clf.fit(X = train_x, y = train_y) # 모델 만들기
모델 구조 살펴보기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.dpi' : '100', # 그래프 크기 설정
'figure.figsize' : [12, 8]}) # 해상도 설정
tree.plot_tree(model); # 그래프 출력
tree.plot_tree(model,
feature_names = train_x.columns, # 예측 변수명
class_names = ['high', 'low'], # 타겟 변수 클래스, 알파벳순
proportion = True, # 비율 표기
filled = True, # 색칠
rounded = True, # 둥근 테두리
impurity = False, # 불순도 표시
label = 'root', # label 표시 위치
fontsize = 10); # 글자 크기
모델을 이용해 예측하기
test_x = df_test.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
test_y = df_test['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
# 예측값 구하기
df_test['pred'] = model.predict(test_x)
df_test
age education_num capital_gain capital_loss hours_per_week workclass_? workclass_Federal-gov workclass_Local-gov workclass_Never-worked workclass_Private ... native_country_Scotland native_country_South native_country_Taiwan native_country_Thailand native_country_Trinadad&Tobago native_country_United-States native_country_Vietnam native_country_Yugoslavia income pred
11712 58 10 0 0 60 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
24768 39 10 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 low low
26758 31 4 0 0 20 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
14295 23 9 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
3683 24 9 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
11985 24 13 0 0 30 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
48445 35 13 10520 0 45 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 high high
19639 41 9 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 high low
21606 29 4 0 0 30 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 low low
3822 31 13 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 low low
14653 rows × 109 columns
성능 평가하기
confusion matrix 만들기
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
labels = ['high', 'low']) # 클래스 배치 순서
conf_mat
array([[ 1801, 1705],
[ 582, 10565]], dtype=int64)
plt.rcParams.update(plt.rcParamsDefault) # 그래프 설정 되돌리기
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
p = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix = conf_mat, # 컨퓨전 매트릭스
display_labels = ('high', 'low')) # 타겟 변수 클래스명
p.plot(cmap = 'Blues') # 컬러맵 적용해 출력
<sklearn.metrics._plot.confusion_matrix.ConfusionMatrixDisplay at 0x15b51553520>
성능 평가 지표 구하기
accuracy
import sklearn.metrics as metrics
metrics.accuracy_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred']) # 예측값
0.8439227461953184
precision
metrics.precision_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
0.7557700377675199
recall
metrics.recall_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
0.5136908157444381
F1 score
metrics.f1_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
0.6116488368143997
정리하기
## 1. 전처리
# 데이터 불러오기
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('adult.csv')
# 1. 타겟 변수 전처리
import numpy as np
df['income'] = np.where(df['income'] == '>50K', 'high', 'low')
# 2. 불필요한 변수 제거하기
df = df.drop(columns = 'fnlwgt')
# 3. 문자 타입 변수를 숫자 타입으로 바꾸기
target = df['income'] # income 추출
df = df.drop(columns = 'income') # income 제거
df = pd.get_dummies(df) # 원핫 인코딩으로 변환
df['income'] = target # df에 target 삽입
# 4. 데이터 분할하기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
df_train, df_test = train_test_split(df,
test_size = 0.3, # 테스트 세트 비율
stratify = df['income'], # 타겟 변수 비율 유지
random_state = 1234) # 난수 고정
## 2. 의사결정나무 모델 만들기
# 모델 설정하기
from sklearn import tree
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 1234, # 난수 고정
max_depth = 3) # 나무 깊이
# 모델 만들기
train_x = df_train.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
train_y = df_train['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
model = clf.fit(X = train_x, y = train_y) # 모델 만들기
# 모델 구조 살펴보기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tree.plot_tree(model,
feature_names = train_x.columns, # 예측 변수명
class_names = ['high', 'low'], # 타겟 변수 클래스, 알파벳순
proportion = True, # 비율 표기
filled = True, # 색칠
rounded = True, # 둥근 테두리
impurity = False, # 불순도 표시
label = 'root', # label 표시 위치
fontsize = 12) # 글자 크기
## 3. 모델을 이용해 예측하기
# 예측하기
test_x = df_test.drop(columns = 'income') # 예측 변수 추출
test_y = df_test['income'] # 타겟 변수 추출
df_test['pred'] = model.predict(test_x) # 예측값 구하기
## 4. 성능 평가하기
# confusion matrix 만들기
from sklearn import metrics
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
labels = ['high', 'low']) # 클래스 배치 순서
# confusion matrix 시각화
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
p = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix = conf_mat, # 컨퓨전 매트릭스
display_labels = ('high', 'low')) # 타겟 변수 클래스명
p.plot(cmap = 'Blues') # 컬러맵 적용해 출력
# accuracy
metrics.accuracy_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred']) # 예측값
# precision
metrics.precision_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
# recall
metrics.recall_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
# F1 score
metrics.f1_score(y_true = df_test['income'], # 실제값
y_pred = df_test['pred'], # 예측값
pos_label = 'high') # 관심 클래스
※ 해당 내용은 <Do it! 파이썬 데이터 분석>의 내용을 토대로 학습하며 정리한 내용입니다.
반응형
'데이터 분석 학습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 16장 데이터를 추출하는 다양한 방법 (2) (0) | 2023.05.11 |
|---|---|
| 16장 데이터를 추출하는 다양한 방법 (1) (1) | 2023.05.10 |
| 15장 머신러닝을 이용한 예측 분석 (1) (0) | 2023.05.08 |
| 14장 통계 분석 기법을 이용한 가설 검정 (2) (0) | 2023.05.07 |
| 14장 통계 분석 기법을 이용한 가설 검정 (1) (0) | 2023.05.06 |



